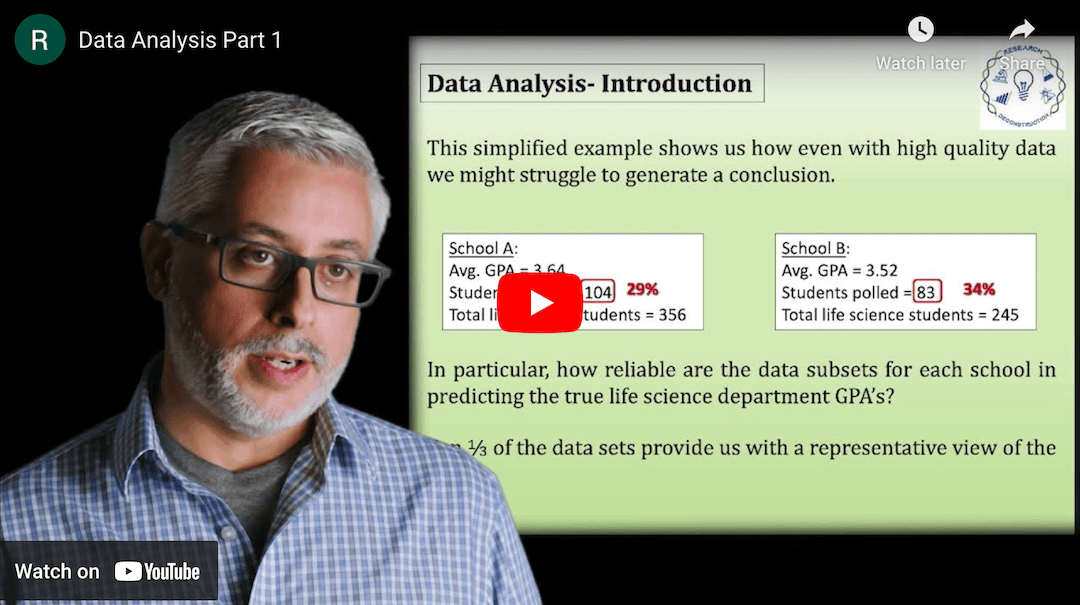
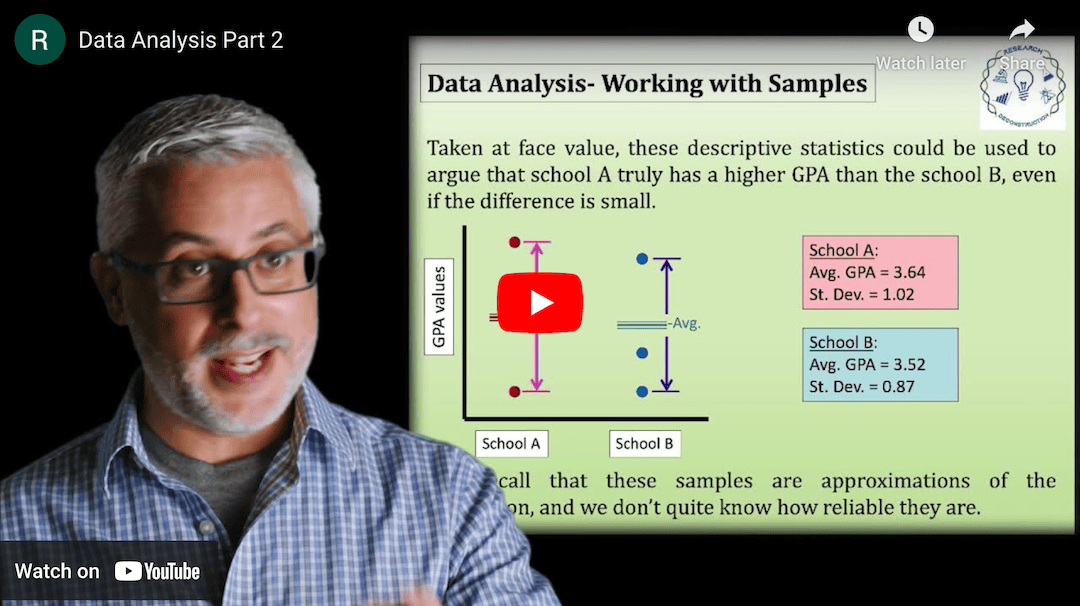
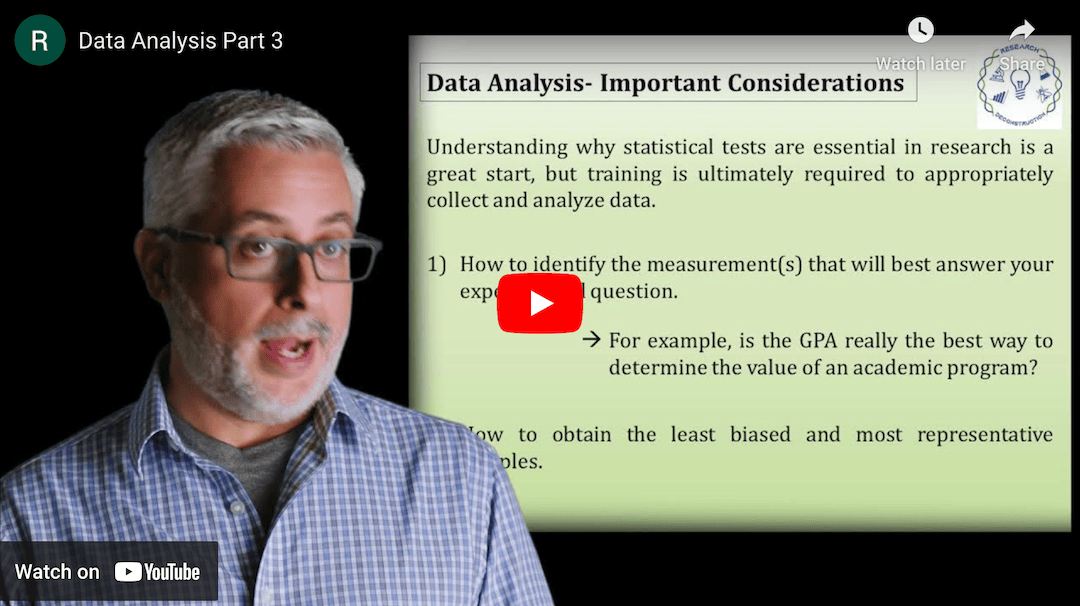
This Research Deconstruction – Introductory Chemistry module contains content designed to be easily added to your biology course: a research seminar video and a series of tutorial videos, as well as sample syllabi as examples for how you might integrate the material with your syllabus. The research seminar provides the source material for the deconstruction. The tutorial videos are intended to support the deconstruction by introducing students to fundamental concepts or techniques used in the research. They can be assigned for pre-class viewing and then reviewed in class during discussion of experiments or other content from the seminar.
These video resources are available at Canvas Commons. An overview of each video is provided below. You can read the overview to decide whether or not the video is relevant to your course.
This material is openly licensed via CC BY-NC-ND 4.0.